The European Space Agency is increasingly looking at possibilities to begin recycling materials in space, as we do every day here on Earth.
The critical words are: recycle, refurbish, repurpose and reuse.
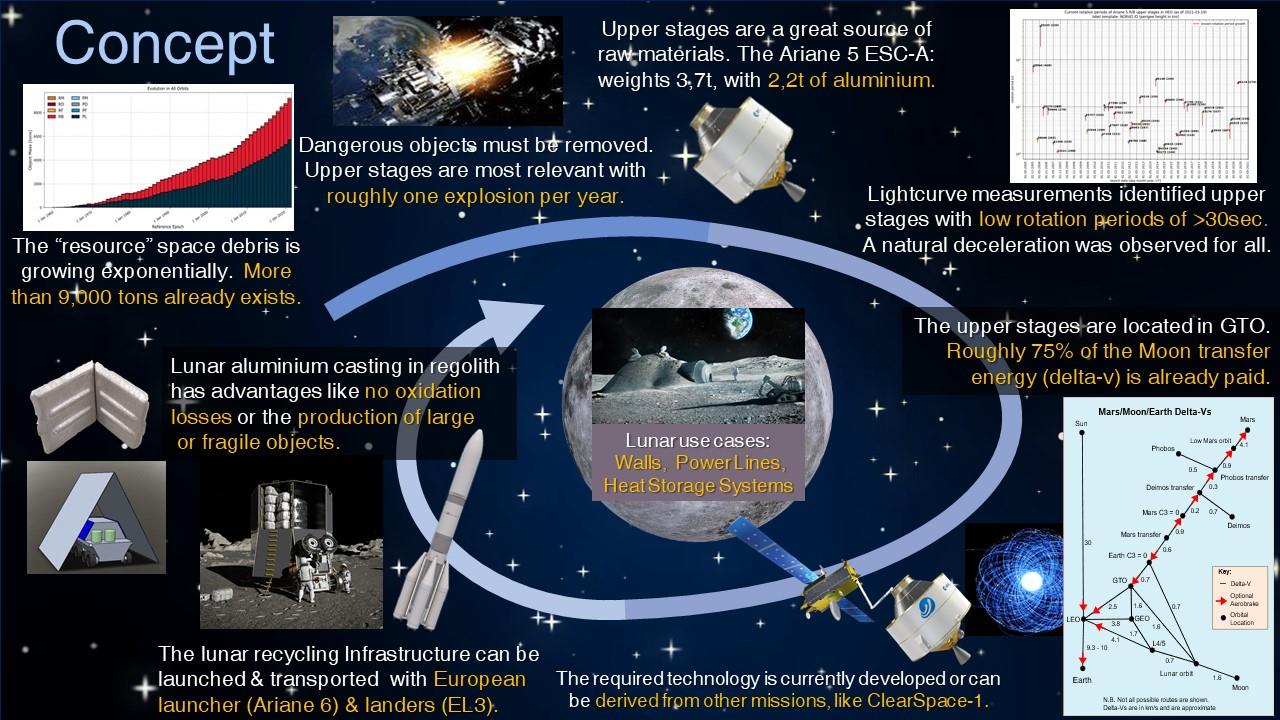
Man has carried in space many tonnes of valuable materials (metals like aluminum and titanium alloys, composite materials etc.) that could be utilized to manufacture and assemble, directly in orbit, next generation orbital and even lunar human bases. For the latter case, recycling could be utilized as a temporary solution before the availability of In-Situ-Resource-Utilization, that is the exploitation of raw lunar materials to self-sustain space constructions.
Orbiting materials have a key feature: they already own high gravitational energy, that was transferred to them during their past launch. This means that such materials do not need to be transferred from Earth surface to orbit, which takes up most of the price per kilogram.
GAUSS was mentioned in one of the last articles of the European Space Agency blog, together with its partners Orbit Recycling and the Fraunhofer FHR TIRA radar.
The article was about ESA‘s intent to became space-debris neutral by 2030 and to implement a “space circular economy” by 2050, by using in-orbit-servicing, that is the process of extend the lifetime of space platforms by refurbishing and replacing space systems that are no more operative, while recycling entire platforms that cannot be reused.
GAUSS, with its CastelGAUSS Space Debris Observatory, is participating in the following Study authored by Orbit Recycling, by collecting orbital and attitude data of specific rocket bodies which could be profitable targets for next in-orbit recycling missions.
Rocket bodies are launchers’ last stages that did not de-orbit after the accomplishment of their mission, and remained in space, typically on a highly elliptical orbits around Earth.
The following video shows Orbit Recycling‘s idea that was submitted to the European Space Agency‘s Discovery Programme, programme reference S 2020-02-b.
